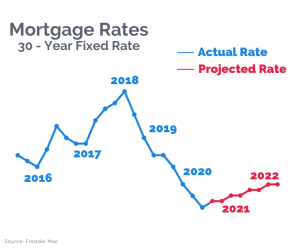
Mortgage rates fluctuate over time as a result of the interaction of the supply and demand for money in the economy. These changes affect the interest rate lenders charge prospective homeowners. By tracking the economic developments that influence mortgage rates, home buyers can understanding how these rates are determined.
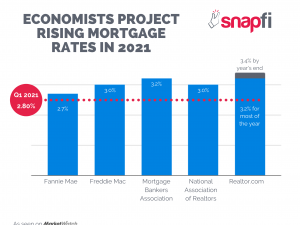
Most experts agree: we saw the historical bottom of the rates back in late 2020 / early 2021, and they are expected to go back up while the economy and housing market stabilizes post COVID-19 pandemic.
Should you refinance or purchase at this time?
Request a quote in 3 mins, no hard credit pull needed:

As rates are expected to increase, it may be a good time to consider what factors make rates go up:
Growth
The economy’s growth varies on inside and outside factors. When there is a low unemployment rate, there is a great indicator that the economy is producing and moving toward growth. But the economy can also be influenced to shrink. Wars or natural disasters (like COVID-19) can hamper the growth rate and potentially shrink the economy. Growth is very sensitive and changes often. When the economy is on a growth path, the demand for money increases and interest rates are pushed upward. The opposite is true when economic growth slows or stops.
Inflation
When there is economic growth, often inflation also occurs. Inflation will increase the price of goods and deteriorates spending power. Inflation can slow growth in the economy. The implication for future homeowners is that inflation pushes mortgage rates higher making the home buying procedure more expensive.
Federal Reserve Board
Economic activity is measured nationally to determine the appropriate interest rate. The Federal Reserve Board, which is the central banking authority in the United States, measures economic growth through 12 Federal Reserve branches across the country. Federal Reserve branches collect economic information from their respective regions and report to the Federal Reserve Board during regular meetings in Washington, D.C. The outcome of this meeting determines whether the Federal Reserve will try to increase interest rates to control growth or decrease rates to spark growth and encourage borrowing.
Money Supply
Although the Federal Reserve is unable to directly set interest rates, the agency can influence rates indirectly by increasing or decreasing the supply of money in the economy. By increasing the money supply, the Federal Reserve puts downward pressure on interest rates. Decreasing the money supply puts upward pressure on interest rates. Consequently, if the Federal Reserve decreases interest rates, mortgage rates come down and borrowing for a home purchase is cheaper and encourages home buying.
Benchmarks
In addition to regular monitoring by the federal government, the financial markets establish benchmarks to understand where interest rates might be headed. The yield on the 10-year treasury bond is widely considered to be a benchmark for long-term mortgage interest rates. As a result, lenders often tie mortgage rates to the 10-year treasury bond to keep the mortgage loan profitable in the long run. Any changes in the 10-year treasury bond yield influence how mortgage rates are set for current mortgages.
Should you buy, cash out, or refinance at this time? It all comes down to dollars and cents.
Use our calculator or request a quote to see how much more we can leave in your pocket:








